| |
Date |
Event(s) |
| 1 | 1841 | |
| 2 | 1843 | - 1843—1843: First Christmas card in England
- 27 May 1843—27 May 1843: The Great Hall of Euston station opened in London
- 19 Jul 1843—19 Jul 1843: Brunel's 'Great Britain' launched
|
| 3 | 1844 | - 6 Jun 1844—6 Jun 1844: YMCA founded in London by Sir George Williams
|
| 4 | 1845 | - 1845—1845: Tarmac laid for first time (in Nottingham)
- 4 Mar 1845—4 Mar 1849:
 James K. Polk U.S. Presidency James K. Polk U.S. Presidency
- 17 Mar 1845—17 Mar 1845: The rubber band patented by Stephen Perry
|
| 5 | 1846 | - 25 Apr 1846—2 Feb 1848:
 Mexican-American War Mexican-American War
- 10 Sep 1846—10 Sep 1846: The sewing machine is patented by Elias Howe
|
| 6 | 1847 | - 1847—1847: US Mormons make Salt Lake City their centre
- Jan 1847—Jan 1847: An anesthetic used for the first time in England (James Simpson used ether to numb the pain of labour)
|
| 7 | 1848 | - 1848—1848: First commercial production of chewing gum
- 24 Jan 1848—24 Jan 1848: Gold found at Sutter's Mill, California - starts the California gold rush
- 11 Jul 1848—11 Jul 1848: Waterloo railway station in London opens
|
| 8 | 1849 | - 1849—1849: Florin (2 shilling coin) introduced as the first step to decimalisation - which finally
occurred in 1971!
- 4 Mar 1849—9 Jul 1850:
 Zachary Taylor U.S. Presidency Zachary Taylor U.S. Presidency
|
| 9 | 1850 | |
| 10 | 1851 | - 1851—1851: Gold discovered in Australia
- 1 May 1851—1 May 1851: Great exhibition of the works of industry of all nations ('Crystal Palace' exhibition) opened in Hyde Park
|
| 11 | 1852 | - 1852—1852: Tasmania ceases to be a convict settlement
- 1852—1852: Wells Fargo established in USA
|
| 12 | 1853 | |
| 13 | 1854 | - 1854—1854: Cigarettes introduced into Britain
- 27 Mar 1854—27 Mar 1854: Britain declares war on Russia (Crimean War)
- 25 Oct 1854—25 Oct 1854: Battle of Balaklava in Crimea (charge of the Light Brigade)
|
| 14 | 1856 | - 1856—1856: End of Crimean War
- 29 Jan 1856—29 Jan 1856: Victoria Cross created by Royal Warrant, backdated to 1854 to recognise acts
during the Crimean War (first award ceremony 26 June 1857)
|
| 15 | 1857 | |
| 16 | 1858 | - 1858—1858: 'The great stink' - smell of the River Thames forced Parliament to stop work
- 1858—1858: Royal Opera House opens in Covent Garden, London
|
| 17 | 1859 | - 1859—1859: Peaceful picketing legalised in Britain
- 25 Apr 1859—25 Apr 1859: Work started on building the Suez canal (opened 17 Nov 1869)
- 4 May 1859—4 May 1859: Brunel's Royal Albert Bridge opened at Saltash giving rail link between Devon
and Cornwall
- 24 Nov 1859—24 Nov 1859: Charles Darwin publishes 'The Origin of Species'
|
| 18 | 1860 | - 29 Aug 1860—29 Aug 1860: First tram service in Europe starts in Birkenhead
|
| 19 | 1861 | |
| 20 | 1862 | - 1862—1862: Lincoln issues first legal US paper money (Greenbacks)
- 20 Apr 1862—20 Apr 1862: First pasteurisation test completed by Louis Pasteur and Claude Bernard
|
| 21 | 1863 | - 1863—1863: Football Association founded (UK)
- 1863—1863: Opening of state institution for criminally insane at Broadmoor, England
- 10 Jan 1863—10 Jan 1863: First section of the London Underground Railway opens
|
| 22 | 1864 | - 1864—1864: A man-powered submarine, 'Hunley' sank a Federal steam ship USS Housatonic at the entrance to Charleston harbour in 1864 - the first recorded successful attack by a submarine on a surface ship
- 11 Mar 1864—11 Mar 1864: The Great Sheffield Flood - over 250 died when a new dam broke while it was being filled for the first time
- 20 Aug 1864—20 Aug 1864: Red Cross established - Twelve nations sign the First Geneva Convention
- 8 Dec 1864—8 Dec 1864: Clifton Suspension Bridge over the River Avon officially opened
|
| 23 | 1865 | - 1865—1865: Elizabeth Garrett Anderson (1836-1917) becomes first woman doctor in England [she later became the first woman mayor in England, in Aldeburgh 1908]
- 1865—1865: First concrete roads built in Britain
- 14 Apr 1865—14 Apr 1865: End of American Civil War - slavery abolished in USA
- 14 Apr 1865—14 Apr 1865: Abraham Lincoln assassinated in Ford's Theatre by John Wilkes Booth
- 15 Apr 1865—4 Mar 1869:
 Andrew Johnson U.S. Presidency Andrew Johnson U.S. Presidency
- 5 Jul 1865—5 Jul 1865: William Booth (1829-1912) founds Salvation Army, in London
|
| 24 | 1867 | - 1 Jul 1867—1 Jul 1867: The British North America Act takes effect, creating the Canadian Confederation
|
| 25 | 1868 | - 1868—1868: Last convicts landed in Australia (Western Australia)
|
| 26 | 1869 | - 1869—1869: Ball bearings, celluloid, margarine, and washing machines, all invented
- 4 Mar 1869—4 Mar 1877:
 Ulysses S. Grant U.S. Presidency Ulysses S. Grant U.S. Presidency
- 23 Nov 1869—23 Nov 1869: Cutty Sark launched in Dumbarton
|
| 27 | 1870 | - 1870—1870: GPO takes over the privately-owned Telegraph Companies (nationalised)
- 1870—1870: Dr Thomas Barnardo opens his first home for destitute children
- 1870—1870: Water closets come into wide use
- 1870—1870: Diamonds discovered in Kimberley, South Africa
- 1 Oct 1870—1 Oct 1870: First British postcard - halfpenny post
|
| 28 | 1871 | - 27 Mar 1871—27 Mar 1871: First Rugby Football international, England v Scotland, played in Edinburgh
- 29 Mar 1871—29 Mar 1871: Opening of Royal Albert Hall, London
- 29 Jun 1871—29 Jun 1871: Trades Unions legalised in Britain, but picketing made illegal
|
| 29 | 1872 | - 1872—1872: Licensing hours introduced
- 1872—1872: Penalties introduced for failing to register births, marriages & deaths (Eng & Wales)
- 4 Dec 1872—4 Dec 1872: American ship 'Mary Celeste' is found abandoned by the British brig 'Dei Gratia' in the Atlantic Ocean
|
| 30 | 1874 | - 1874—1874: Factory Act introduces 56-hour week
- 5 Apr 1874—5 Apr 1874: Birkenhead Park opened, said to be the first civic public park in the world - features of it later copied in Central Park, New York
|
| 31 | 1875 | - 1875—1875: London's main sewage system completed
- 1 Jan 1875—1 Jan 1875: Midland Railway abolishes Second Class passenger facilities, leaving First Class and Third Class. Other British railway companies followed during the rest of the year. (Third Class was renamed Second Class in 1956)
|
| 32 | 1876 | - 14 Feb 1876—14 Feb 1876: Alexander Graham Bell and Elisha Gray each file a patent for the telephone - Bell awarded the rights
|
| 33 | 1877 | |
| 34 | 1878 | - 1878—1878: Edison & Swan invent electric lamp
- 1878—1878: Red Flag Act in Britain limits mechanical road vehicles to 4mph
- 1878—1878: CID established at New Scotland Yard
|
| 35 | 1879 | - 18 Sep 1879—18 Sep 1879: Blackpool illuminations switched on for first time
|
| 36 | 1880 | - 1880—1880: Education Act: schooling compulsory for 5-10 year olds
- 1880—1880: Mosquito found to be the carrier of malaria
- 2 Aug 1880—2 Aug 1880: Greenwich Mean Time adopted throughout UK
|
| 37 | 1881 | - 1881—1881: Postal Orders introduced
- 1881—1881: Flogging abolished in Army and Royal Navy
- 4 Mar 1881—19 Sep 1881:
 James A. Garfield U.S. Presidency James A. Garfield U.S. Presidency
- Sep 1881—Sep 1881: Godalming in Surrey became the first town in England to have a public electricity
supply installed (but in 1884 it reverted to gas lighting until 1904)
- 19 Sep 1881—4 Mar 1885:
 Chester A. Arthur U.S. Presidency Chester A. Arthur U.S. Presidency
- 26 Oct 1881—26 Oct 1881: Gunfight at OK Corral
|
| 38 | 1882 | - 1882—1882: Fourth Eddystone Lighthouse completed
|
| 39 | 1883 | - 1883—1883: Statue of Liberty presented to USA by France
- 24 May 1883—24 May 1883: Brooklyn Bridge, New York opens (crosses East River)
- 1 Aug 1883—1 Aug 1883: Parcel post starts in Britain
- 27 Aug 1883—27 Aug 1883: Eruption of Krakatoa near Java - 30,000 killed by tidal wave
|
| 40 | 1884 | - 31 May 1884—31 May 1884: John Harvey Kellogg patents corn flakes
- 13 Oct 1884—13 Oct 1884: Greenwich made prime meridian of the world
|
| 41 | 1885 | - 1885—1885: Carl Benz builds the 'Motorwagen', a single-cylinder motor car
- 1885—1885: Gottlieb Daimler patents the world's first motorcycle
- 1885—1885: Eastman makes first coated photographic paper
- 1885—1885: Canadian Pacific Railway completed
- Mar 1885—Mar 1885: First UK cremation in modern times took place at Woking
- 4 Mar 1885—4 Mar 1889:
 Grover Cleveland U.S. Presidency Grover Cleveland U.S. Presidency
- 5 Sep 1885—5 Sep 1885: The first train runs through the Severn Tunnel
- 29 Sep 1885—29 Sep 1885: First electric tramcar used at Blackpool
|
| 42 | 1886 | - 20 Jan 1886—20 Jan 1886: Mersey railway (under Mersey) opened by Prince of Wales
- May 1886—May 1886: Pharmacist John Styth Pemberton invents a carbonated beverage later named 'Coca-Cola'
- 29 May 1886—29 May 1886: Putney Bridge opens in London
|
| 43 | 1887 | - 1887—1887: Daimler produces a four-wheeled motor car
|
| 44 | 1888 | - 1888—1888: Convention of Constantinople guarantees free maritime passage through Suez Canal in war and peace
- 1888—1888: Jack the Ripper active in east London during the latter half of the year
- 1888—1888: County Councils set up in Britain
- 1888—1888: Dunlop invents pneumatic tyre
- 1888—1888: First box camera - George Eastman registers the trademark Kodak, and receives a patent
for his camera which uses roll film
- 20 Mar 1888—20 Mar 1888: Football League formed
|
| 45 | 1889 | - 1889—1889: Celluloid film produced
- 1889—1889: Dock Strike - docker's won their 'Docker's Tanner' 6 old pennies
- 4 Mar 1889—4 Mar 1893:
 Benjamin Harrison U.S. Presidency Benjamin Harrison U.S. Presidency
- 31 Mar 1889—31 Mar 1889: Eiffel Tower completed (to mark centenary of French Revolution)
- 14 May 1889—14 May 1889: Children's charity NSPCC launched in London
- 3 Jun 1889—3 Jun 1889: Canadian Pacific Railway completed from coast to coast
- 28 Sep 1889—28 Sep 1889: Length of a metre defined
|
| 46 | 1890 | - 4 Mar 1890—4 Mar 1890: Forth railway bridge opens - took six years to build
- 4 Nov 1890—4 Nov 1890: City & South London Railway opens - London's first deep-level tube railway
and first major railway in the world to use electric traction
|
| 47 | 1891 | - 1891—1891: Primary education made free and compulsory
- 18 Mar 1891—18 Mar 1891: First telephone link between London & Paris
- 4 May 1891—4 May 1891: Fictional date when Sherlock Holmes throws Moriarty over Reichenbach Falls, then disappears for 3 years! (published in 1893)
- 24 Aug 1891—24 Aug 1891: Thomas Edison patents the motion picture camera
|
| 48 | 1892 | - 1892—1892: Electric oven invented
- 1892—1892: Shop Hours Act - limit 74 hours per week for under-18's
- 6 Oct 1892—6 Oct 1892: Alfred Lord Tennyson dies, aged 83, at his house Aldworth, near Haslemere
|
| 49 | 1893 | |
| 50 | 1894 | - 1894—1894: Picture postcard introduced in Britain
- 1 Jan 1894—1 Jan 1894: Manchester Ship Canal opens
- 1 Mar 1894—1 Mar 1894: Blackpool Tower opens
- 30 Jun 1894—30 Jun 1894: Tower Bridge first opens
- 2 Aug 1894—2 Aug 1894: Death duties first introduced in Britain
|
| 51 | 1895 | - 1895—1895: Sir Henry Wood starts Promenade Concerts in London
- 12 Jan 1895—12 Jan 1895: The National Trust founded in England
- 24 May 1895—24 May 1895: Henry Irving becomes the first person from the theatre to be knighted
- 28 May 1895—28 May 1895: Oscar Wilde sent to prison
- 12 Jul 1895—12 Jul 1895: First recorded motor journey of any length (56 miles) in Britain
- 17 Oct 1895—17 Oct 1895: First people in Britain to be charged with motor offences - John Henry Knight and James Pullinger of Farnham, Surrey
- Nov 1895—Nov 1895: X-rays discovered
|
| 52 | 1896 | - 5 Apr 1896—5 Apr 1896: First modern Olympic Games held in Athens
- 2 Jun 1896—2 Jun 1896: Guglielmo Marconi receives a British patent (later disputed) for the radio
|
| 53 | 1897 | |
| 54 | 1898 | - 1898—1898: First photograph using artificial light
- 1898—1898: Zeppelin builds airship
- 1898—1898: Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company founded
- 17 Mar 1898—17 Mar 1898: USS Holland launched, the first practical submarine
- 21 Apr 1898—13 Aug 1989:
 Spanish-American War Spanish-American War
- 27 Jun 1898—27 Jun 1898: The first solo circumnavigation of the globe completed at Rhode island by
Joshua Slocum in Spray (started from Boston, Mass on Apr 24, 1895)
|
| 55 | 1899 | - 4 Feb 1899—2 Jul 1902:
 Philippine-American War Philippine-American War
- 6 Mar 1899—6 Mar 1899: Aspirin first marketed by Bayer
- 11 Oct 1899—11 Oct 1899: Start of Second Boer War
- 18 Oct 1899—7 Sep 1901:
 Boxer Rebellion Boxer Rebellion
|
| 56 | 1900 | - 1900—1900: School leaving age in Britain raised to 14 years
- 1900—1900: Central Line opens in London: underground is electrified
- 1900—1900: Escalator shown at Paris exhibition
- 9 Feb 1900—9 Feb 1900: Davis Cup tennis competition established
- 27 Feb 1900—27 Feb 1900: Labour Party formed
|
| 57 | 1901 | - 1901—1901: Commonwealth of Australia founded
- 1901—1901: Hubert Cecil Booth patents the vacuum cleaner
- 22 Jan 1901—22 Jan 1901: Queen Victoria dies - Edward VII king
- 2 Feb 1901—2 Feb 1901: Queen Victoria's funeral - interred beside Prince Albert in the Frogmore
Mausoleum at Windsor Great Park
- Jun 1901—Jun 1901: Denunciation of use of concentration camps by British in Boer War
- 14 Sep 1901—4 Mar 1909:
 Theodore Roosevelt U.S. Presidency Theodore Roosevelt U.S. Presidency
- 2 Oct 1901—2 Oct 1901: Britain's first submarine launched
- 12 Dec 1901—12 Dec 1901: First successful radio transmission across the Atlantic, by Marconi - Morse
code from Cornwall to Newfoundland
|
| 58 | 1902 | - 1902—1902: Balfour's Education Act provides for secondary education
- 1902—1902: Cremation Act - cremation can only take place at officially recognised establishments,
and with two death certificates issued
- 1902—1902: Marie Curie discovers radioactivity
- 24 May 1902—24 May 1902: Empire Day (later Commonwealth Day) first celebrated
- 31 May 1902—31 May 1902: Treaty of Vereeniging ends Second Boer War
- 9 Aug 1902—9 Aug 1902: Coronation of Edward VII
|
| 59 | 1903 | - 1903—1903: Workers' Education Association (WEA) formed in Britain
- 1903—1903: Women's Social and Political Union formed in Britain by Emmeline Pankhurst
- 1903—1903: Henry Ford sets up his motor company
- 14 Dec 1903—14 Dec 1903: First flight of Wilbur & Orville Wright
- 17 Dec 1903:
 First Flight First Flight
|
| 60 | 1904 | - 1904—1904: Leeds University established
- 8 Apr 1904—8 Apr 1904: France and UK sign the Entente Cordiale
- 4 May 1904—4 May 1904: America takes over construction of the Panama Canal from the French
(completed 1914)
|
| 61 | 1905 | - 1905—1905: The title 'Prime Minister' noted in a royal warrant for the first time - placed the Prime
Minister in order of precedence in Britain immediately after the Archbishop of York
- 1905—1905: Aliens Act in Britain: Home Office controls immigration
- 1905—1905: Germany lays down the first Dreadnought battleship
- 11 Apr 1905—11 Apr 1905: Einstein publishes Special Theory of Relativity
|
| 62 | 1906 | - 1906—1906: Introduction of free school meals for poor children
- 10 Feb 1906—10 Feb 1906: Launching of HMS Dreadnought, first turbine-driven battleship
- 15 Mar 1906—15 Mar 1906: Rolls-Royce Ltd registered
- 26 May 1906—26 May 1906: Vauxhall Bridge opened in London
- 20 Sep 1906—20 Sep 1906: Launching of Cunard's RMS Mauretania on the Tyne
|
| 63 | 1907 | - 1907—1907: New Zealand becomes a Dominion
- 1907—1907: Imperial College, London, is established
- 1907—1907: First airship flies over London
- 1907—1907: Lumiere develops a process for colour photography
- Jul 1907—Jul 1907: Leo Hendrik Baekeland patents Bakelite, the first plastic invented that held its
shape after being heated
- 1 Aug 1907—1 Aug 1907: Baden-Powell leads the first Scout camp on Brownsea Island
- 9 Nov 1907—9 Nov 1907: The Cullinan Diamond presented to Edward VII on his birthday
|
| 64 | 1908 | - 1908—1908: Coal Mines Regulation Act in Britain limits men to an eight hour day
- 1908—1908: Separate courts for juveniles established in Britain
- 1908—1908: Lord Baden-Powell starts the Boy Scout movement
- 1908:
 Model T Model T
- 1 Jul 1908—1 Jul 1908: SOS became effective as an international signal of distress
- 12 Aug 1908—12 Aug 1908: First 'Model T' Ford made
|
| 65 | 1909 | - 1909—1909: Beveridge Report prompts creation of labour Exchanges
- 1909—1909: Peary reaches the north pole
- 1909—1909: First commercial manufacture of Bakelite - start of the plastic age
- 1 Jan 1909—1 Jan 1909: Old Age Pensions Act came into force
- 16 Jan 1909—16 Jan 1909: Ernest Shackleton's expedition finds the magnetic South Pole
- 4 Mar 1909—4 Mar 1913:
 William Howard Taft U.S. Presidency William Howard Taft U.S. Presidency
- 15 Mar 1909—15 Mar 1909: Selfridges department store opens in London
- 25 Jul 1909—25 Jul 1909: Bleriot flies across the Channel (36 minutes, Calais to Dover)
|
| 66 | 1910 | - 1910—1910: Railway strike and coal strikes in Britain
- 1910—1910: Constitutional crisis in Britain
- 1910—1910: Dr Crippen caught by radio telegraphy; hanged 23 Nov at Pentonville
- 1910—1910: Madame Curie isolates radium
- 1910—1910: Halley's comet reappears
- 1910—1910: Tango becomes popular in North America and Europe
- 6 May 1910—6 May 1910: Edward VII dies - George V becomes King
|
| 67 | 1911 | - 1911—1911: Parliament Act in Britain reduces the power of the House of Lords
- 1911—1911: British MPs receive a salary
- 1911—1911: First British Official Secrets Act
- 1911—1911: Rutherford: theory of atomic structures
- 1911—1911: Strikes by seamen, dock and transport workers (1911-1912)
- 2 Apr 1911—2 Apr 1911: Census: Population - England and Wales: 36 Million; Scotland: 4.6 Million; N Ireland: 1.25 Million
- 22 Jun 1911—22 Jun 1911: Coronation of George V
- 14 Dec 1911—14 Dec 1911: National Insurance introduced in Britain
|
| 68 | 1912 | - 1912—1912: Irish Home Rule crisis grows in Britain
- 1912—1912: Britain nationalises the telephone system
- 1912—1912: Discovery of the 'Piltdown Man' - hoax, exposed in 1953
- 18 Jan 1912—18 Jan 1912: Captain Scott's last expedition - he and his team reach the south pole on Jan
18th; all die on the way back, their bodies found in November
- 14 Apr 1912—14 Apr 1912: The 'unsinkable' Titanic sinks on maiden voyage - loss of 1,513 lives
- 15 Apr 1912:
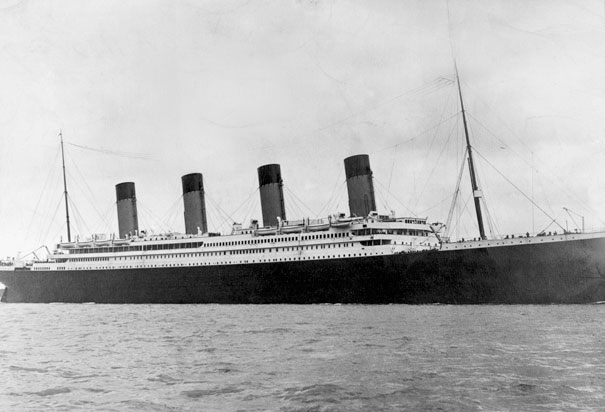 Titanic Sinks Titanic Sinks
- 13 May 1912—13 May 1912: Royal Flying Corps (later the RAF) founded in Britain
|
| 69 | 1913 | - 1913—1913: Third Irish Home Rule Bill rejected by House of Lords - threat of civil war in Ireland -
formation of Ulster Volunteers to oppose Home Rule
- 1913—1913: Suffragette demonstrations in London - Mrs Pankhurst imprisoned
- 1913—1913: Trade Union Act in Britain establishes the right to use Union funds for political
purposes
- 1913—1913: Invention of stainless steel by Harry Brearley of Sheffield
- 1913—1913: Geiger invents his counter to measure radioactivity
- 4 Mar 1913—4 Mar 1921:
 Woodrow Wilson U.S. Presidency Woodrow Wilson U.S. Presidency
- 4 Jun 1913—4 Jun 1913: Emily Davison, a suffragette, runs out in front of the king's horse, Anmer, at the
Epsom Derby and dies
|
| 70 | 1914 | - 1914—1914: Irish Home Rule Act provides for a separate Parliament in Ireland; the position of Ulster
to be decided after the War
- 1914—1914: Chaplin and De Mille make their first films
- 28 Jun 1914—28 Jun 1914: Archduke Ferdinand assassinated in Sarajevo
- 28 Jul 1914—11 Nov 1918:
 World War I World War I
- 4 Aug 1914—4 Aug 1914: Britain declares war on Germany, citing Belgian neutrality as reason
- 5 Aug 1914—5 Aug 1914: British cableship Telconia cut through all five of Germany's undersea telegraph
links to the outside world
- 15 Aug 1914—15 Aug 1914: Panama Canal opened, the Canal cement boat 'Ancon' making the first official
transit (plans for a grand opening were cancelled due to the start of WW1)
- Oct 1914—Oct 1914: Battle of Ypres - beginning of trench warfare on western front
- 27 Nov 1914—27 Nov 1914: First policewoman goes on duty in Britain
- 16 Dec 1914—16 Dec 1914: German battleships bombard Hartlepool and Scarborough
|
| 71 | 1915 | - 1915—1915: Junkers construct first fighter aeroplane
- 1915—1915: First automatic telephone exchange in Britain
- 19 Jan 1915—19 Jan 1915: First Zeppelin air raid on England, over East Anglia - four killed
- Feb 1915—Feb 1915: Submarine blockade of Britain starts
- Apr 1915—Apr 1915: Second Battle of Ypres - poison gas used for first time
- 25 Apr 1915—25 Apr 1915: Gallipoli campaign starts (declared ANZAC Day in 1916)
- 7 May 1915—7 May 1915: RMS Lusitania sunk by German submarine off coast of Ireland - 1,198 died
- 16 May 1915—16 May 1915: First meeting of a British WI (Women's Institute) took place in Llanfairpwll
(aka Llanfair PG), Anglesey
|
| 72 | 1916 | - 1916—1916: Compulsory military service introduced in Britain
- Feb 1916—Feb 1916: Battle of Verdun - appalling losses on both sides, stalemate continues
- 24 Apr 1916—24 Apr 1916: Easter Rising in Ireland - after the leaders are executed, public opinion backs
independence
- 21 May 1916—21 May 1916: First use of Daylight Saving Time in UK
- 31 May 1916—31 May 1916: Battle of Jutland - only major naval battle between the British and
German fleets
- 5 Jun 1916—5 Jun 1916: Sinking of HMS Hampshire and death of Kitchener
- 3 Aug 1916—3 Aug 1916: Sir Roger Casement hanged at Pentonville Prison for treason
- 15 Sep 1916—15 Sep 1916: First use of tanks in battle, but of limited effect (Battle of the Somme 1 July to 18 Nov: over 1 million casualties)
- 7 Dec 1916—7 Dec 1916: Lloyd-George becomes British Prime Minister of the coalition government
|
| 73 | 1917 | - 1917—1917: Battle of Cambrai - first use of massed tanks, but effect more psychological than actual
- 1917—1917: Ministry of Labour is established in Britain
- Feb 1917—Feb 1917: February revolution in Russia; Tsar Nicholas abdicates
- 16 Apr 1917—16 Apr 1917: Lenin returns to Russia after exile
- 17 Apr 1917—17 Apr 1917: USA declares war on Germany
- 26 May 1917—26 May 1917: George V changes surname from Saxe-Coburg-Gotha to Windsor (Royal
proclamation on 17 July)
- Jul 1917—Jul 1917: Battle of Passchendaele - little gained by either side (Jul-Nov)
- 7 Nov 1917—7 Nov 1917: 'October' Revolution in Russia - Bolsheviks overthrow provisional government;
Lenin becomes Chief Commissar
- 6 Dec 1917—6 Dec 1917: Halifax (Nova Scotia) Explosion, one of the world's largest artificial non-nuclear
explosions to date: a ship loaded with wartime explosives blew up after a collision,
obliterating buildings and structures within two square kilometres of the explosion
- 9 Dec 1917—9 Dec 1917: British forces capture Jerusalem
|
| 74 | 1918 | - 1918—1918: Vote for women over 30, men over 21 (except peers, lunatics and felons)
- 1918—1918: War of Independence in Ireland
- 18 Jan 1918—18 Jan 1918: Bentley Motors founded
- 8 Mar 1918—8 Mar 1918: Start of world-wide 'flu pandemic
- Jul 1918—Jul 1918: Second Battle of the Marne: last major German offensive in WW1 (Jul-Aug)
- 1 Oct 1918—1 Oct 1918: Arab forces under Lawrence of Arabia capture Damascus
- 11 Nov 1918—11 Nov 1918: Armistice signed
- Dec 1918—Dec 1918: First woman elected to House of Commons, Countess Markiewicz as a Sinn Fein
member refused to take her seat
|
| 75 | 1919 | - 1919—1919: Britain adopts a 48-hour working week
- 1919—1919: Sir Ernest Rutherford publishes account of splitting the atom
- 15 Jun 1919—15 Jun 1919: Alcock and Brown complete first nonstop flight across the Atlantic
- 28 Jun 1919—28 Jun 1919: Treaty of Versailles signed
|
| 76 | 1920 | - 1920—1920: Regular cross-channel air service starts
- 1920—1920: Marconi opens a radio broadcasting station in Britain
- 1920—1920: Thompson patents his machine gun (Tommy gun)
- Feb 1920—Feb 1920: First roadside petrol filling station in UK - opened by the Automobile Association
at Aldermaston on the Bath Road
|
| 77 | 1921 | - 1921—1921: Railway Act in Britain amalgamates companies - only four remained
- 1921—1921: Insulin discovery announced
- 1921—1921: First birth control clinic
- 4 Mar 1921—2 Aug 1923:
 Warren G. Harding U.S. Presidency Warren G. Harding U.S. Presidency
- 19 Jun 1921—19 Jun 1921: Census: Population - England and Wales: 37.9 Million; Scotland: 4.9 Million; N Ireland: 1.25 Million
- 6 Dec 1921—6 Dec 1921: Anglo-Irish Treaty signed in London, leading to the formation of the Irish Free
State and Northern Ireland
|
| 78 | 1922 | - 1922—1922: Law of Property Act - the manorial system effectively ended
- 1 Jun 1922—1 Jun 1922: Royal Ulster Constabulary founded
- Oct 1922—Oct 1922: BBC established as a monopoly, and begins transmissions in November (2LO in
London on 14 Nov; 5IT in Birmingham and 2ZY in Manchester on 15 Nov)
|
| 79 | 1923 | - 1923—1923: Roads in Great Britain classified with A and B numbers
- 1923—1923: Hubble shows there are galaxies beyond the Milky Way
- 1923—1923: First American broadcasts heard in Britain
- 1 Jan 1923—1 Jan 1923: The majority of the railway companies in Great Britain grouped into four main
companies, the Big Four: LNER, GWR, SR, LMSR - lasted until nationalisation in 1948
- 16 Feb 1923—16 Feb 1923: Howard Carter unsealed the burial chamber of Tutankhamun
- 28 Apr 1923—28 Apr 1923: First Wembley cup final (West Ham 0, Bolton 2) - 'I'm Forever Blowing Bubbles ' popular song of the time became the West Ham anthem
- 2 Aug 1923—4 Mar 1929:
 Calvin Coolidge U.S. Presidency Calvin Coolidge U.S. Presidency
- 28 Sep 1923—28 Sep 1923: First publication of Radio Times
|
| 80 | 1924 | - 4 Jan 1924—4 Jan 1924: First Labour government in Britain, headed by Ramsay MacDonald
- 5 Feb 1924—5 Feb 1924: Hourly Greenwich Time Signals from the Royal Greenwich Observatory were
first broadcast by the BBC
- 31 Mar 1924—31 Mar 1924: British Imperial Airways begins operations (formed by merger of four British
airline companies - became BOAC in 1940)
|
| 81 | 1925 | - 1925—1925: Britain returns to gold standard
- 18 Jul 1925—18 Jul 1925: Adolf Hitler publishes Mein Kampf
|
| 82 | 1926 | - 1926—1926: First public demonstration of television (TV) by John Logie Baird
- 1926—1926: Adoption of children is legalised in Britain
- 1926—1926: Kodak produces 16mm movie film
- 1926—1926: Walt Disney arrives in Hollywood
- 21 Apr 1926—21 Apr 1926: Princess Elizabeth born
- 3 May 1926—3 May 1926: General Strike begins. Lasts until May 12 (mine workers for 6 months more)
- 31 Oct 1926—31 Oct 1926: Death of Harry Houdini
|
| 83 | 1927 | - 1927—1927: Release of the first 'talkie' film (The Jazz Singer)
- 7 Jan 1927—7 Jan 1927: First transatlantic telephone call - New York City to London
- 22 Jan 1927—22 Jan 1927: First football broadcast by BBC (Arsenal v Sheffield United at Highbury)
- 1 May 1927—1 May 1927: First cooked meals on a scheduled flight introduced by Imperial Airways from
London to Paris
- 20 May 1927—20 May 1927: Lindbergh makes solo flight across the Atlantic, in 33? hours
- 31 May 1927—31 May 1927: Last Ford Model T rolls off assembly line
- 24 Jul 1927—24 Jul 1927: The Menin Gate war memorial unveiled at Ypres
|
| 84 | 1928 | - 1928—1928: Women over 21 get vote in Britain - same qualification for both sexes
- 26 Apr 1928—26 Apr 1928: Madame Tussauds opens in London
- 15 Sep 1928—15 Sep 1928: Sir Alexander Fleming accidentally discovers penicillin (results published 1929)
|
| 85 | 1929 | - 1929—1929: Abolition of Poor Law system in Britain
- 1929—1929: Minimum age for a marriage in Britain (which had been 14 for a boy and 12 for a girl)
now 16 for both sexes, with parental consent (or a licence) needed for anyone under 21
- 1929—1929: BBC begins experimental TV transmissions
- 4 Mar 1929—4 Mar 1933:
 Herbert Hoover U.S. Presidency Herbert Hoover U.S. Presidency
|



 Submit Photo / Document
Submit Photo / Document
